Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO2) Powder


Lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2 or LCO), CAS number 12190-79-3, is a benchmark battery material that replaces lithium metal as cathode for greater stability and capacity. This high performance LCO cathode material dominates in computer, communication, and consumer electronics-based lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) with the merits of easy procession, unprecedented volumetric and gravimetric energy density, and high operation potential.
LiCoO2 possesses a high theoretical specific capacity (274 mAh/g) and high discharge voltage (~4.2 V vs Li+/Li). However, when half of the Li+ are removed roughly at 4.0 − 4.2 V, it causes an abrupt change in configurational entropy (ΔS) and leads to structural instability. Consequently, commercial LiCoO2 exhibits a maximum capacity of only ~165 mAh/g.
| CAS Number | 12190-79-3 |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | LiCoO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 97.87 g/mol |
| Chemical Name | Lithium Cobalt Oxide |
| Synonyms | Lithium cobaltite |
| Classification / Family | 2D semiconducting materials, Battery materials, Metal oxides, Cathode materials |
| Colour | Black to grey powder |
| Product Code | M2401A1 |
|---|---|
| Average Particle Size (APS) | D50: ~ 10 μm |
| Specific Surface Area (SSA) | 0.2 – 0.5 m2/g |
| Coin Cell Capacity 1 C (3.0 – 4.3 V) | ≥151 mAh/g |
| True Density | 2.8 g/cm3 |
| Li Content (%) | 6.9 – 7.1 |
| Co Content (%) | 59 – 61 |
| pH | 9 – 11 |
The crystal structure of LiCoO2 consists of cobalt atoms that are in the trivalent oxidation state (Co3+), sandwiched between two layers of oxygen atoms. Parallel layers of monovalent lithium cations (Li+) lie between extended anionic sheets of cobalt and oxygen atoms.
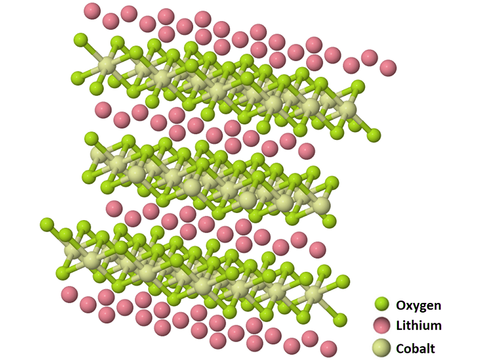 Lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) layered structure, CAS 12190-79-3-1
Lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) layered structure, CAS 12190-79-3-1
专业代理国外知名镊子品牌
我们将竭诚为你服务
0755-23003036