Holey Graphene


Holey graphene (hG; CAS number 1034343-98-0), defined as a periodic array of holes in the regular single layer of carbon atoms, is created via facile microscopic engineering to generate holes in basal planes of graphene-based materials. The holes can disrupt the continuous of carbon honeycomb structure and cause an energy bandgap to open up around the baseline energy level of the material, tuning the graphene into a semiconductor. Holey graphene thus possesses high surface area, abundant ion binding sites, enhanced ion diffusion kinetics, and excellent high-rate lithium-ion storage capabilities. It outperforms its pristine form, graphene, in various fields of applications especially in capacitors, fuel cells, and Li-ion and Na-ion batteries.
The lack of continuous carbon weakens the interlayer attractive forces i.e., the van der Waals interactions among the layers with increased interlayer distance among the sheets. The availability of a large number of pores and increased interlayer distance provide a boost to the ion movement and enhanced mass transport to also promote applications in water purification and sensors.
| CAS Number | 1034343-98-0 |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C |
| Molecular Weight | 12.01 g/mol |
| Synonyms | Porous Graphene, Perforated Graphene |
| Classification or Family | 2D semiconducting materials, Carbon nanomaterials, Nanomaterials, Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, Energy Storage, Supercapacitors, Organic photovoltaics (OPV), Organic electronics |
| Form | Black Powder |
| Product Code | M2406A1 |
|---|---|
| Sheet Resistance | 602 Ω/m2 |
| Volume Resistance | 0.06 Ω cm |
| Electrical Conductivity | >800 S/m |
| Pore Size | >50 nm |
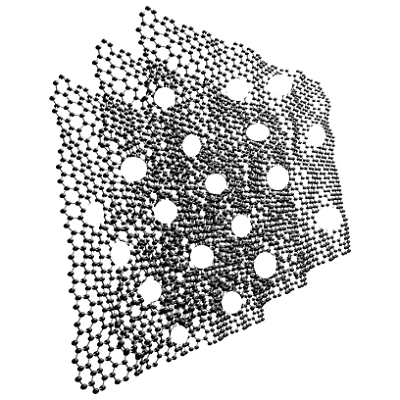 Holey graphene structure, CAS 1034343-98-0
Holey graphene structure, CAS 1034343-98-0
专业代理国外知名镊子品牌
我们将竭诚为你服务
0755-23003036