N,N′-Di(1-naphthyl)-N,N′-diphenyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4,4′-diamine, also known as NPB or NPD, has been used intensively in OLEDs and other organic electronic devices such as polymer photovoltaics (OPV) and perovskite solar cells for its outstanding hole transport capability.
NPB is considered as one of the best materials within its competition, and has become the most common-used material in OLEDs' application. This is due to its increased Tg up to 95 °C, which enhances device morphology and is beneficial for device longevity [1].
General Information
|
CAS number
|
123847-85-8
|
|
Chemical formula
|
C44H32N2
|
|
Molecular weight
|
588.74 g/mol
|
|
HOMO/LUMO
|
HOMO = 5.5 eV, LUMO = 2.4 eV
|
|
Absorption*
|
λmax 339 nm
|
|
Fluorescence
|
λem 450 nm (in THF)
|
|
Synonyms
|
-
NPB, NPD
-
N,N′-Di(1-naphthyl)-N,N′-diphenyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4,4′-diamine
-
N,N′-Bis(naphthalen-1-yl)-N,N′-bis(phenyl)benzidine
|
|
Classification / Family
|
Triphenylamines, Naphtalene, Hole-transport layer materials, Electron block layer materials, Hole-injection layer materials, Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), OFETs, Organic Photovoltaics, Polymer solar cells, Perovskite solar cells
|
* Measurable with an USB spectrometer, see our spectrometer application notes.
Product Details
|
Purity
|
> 99.5% (sublimed)
> 98.0% (unsublimed)
|
|
Melting point
|
279-283 °C (lit.)
|
|
Appearance
|
Off-White powder
|
* Sublimation is a technique used to obtain ultra pure-grade chemicals, see sublimed materials.
Chemical Structure
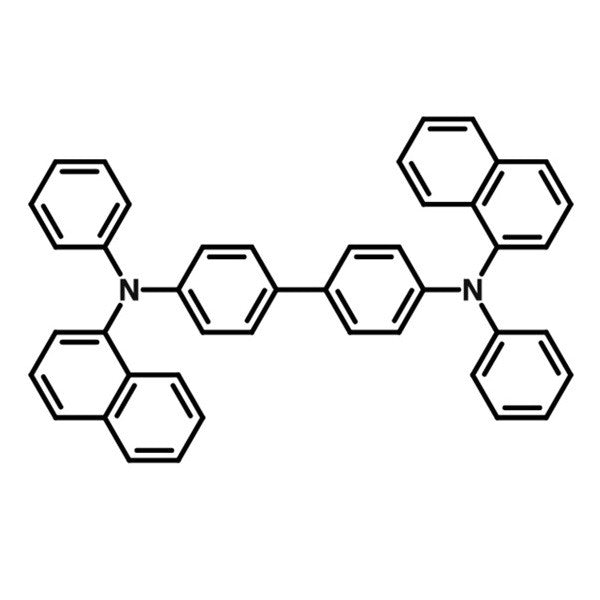 Chemical structure of N,N′-Di(1-naphthyl)-N,N′-diphenyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4,4′-diamine (NPB)
Chemical structure of N,N′-Di(1-naphthyl)-N,N′-diphenyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4,4′-diamine (NPB)
Device Structure(s)
|
Device structure
|
ITO/NPB (30 nm)/NPB: DCJTB: C545T* (10 nm)/NPB (4 nm)/DNA (8 nm)/(BCP) (9 nm)/Alq3 (30 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al (100 nm) [2]
|
|
Colour
|
White 
|
|
Max. Luminance
|
13,600 cd/m2
|
|
Max. Current Efficiency
|
12.3 cd/A
|
|
Max. Power Efficiency
|
4.4 lm W−1
|
|
Device structure
|
ITO/MoO3 (7nm)/NPB (85 nm)/ (PPQ)2Ir(acac):Ir(ppy)3:FIrpic:mCP/TAZ/LiF/Al [3]
|
|
Colour
|
White 
|
|
Max. EQE
|
20.1%
|
|
Max. Power Efficiency
|
41.3 lm W−1
|
|
Device structure
|
ITO/PEDOT:PSS/NPB/mCP/FPt*(1.5 nm)/OXD-7/CsF/Al [4]
|
|
Colour
|
White 
|
|
Max. EQE
|
17.5%
|
|
Max. Power Efficiency
|
45 lm W−1
|
|
Device structure
|
ITO/2-TNATA:33% WO3 (100 nm)/NPB (10 nm)/Alq3 (30 nm)/Bphen (20 nm)/BPhen: 2% Cs (10 nm)/Al (150 nm) [5]
|
|
Colour
|
Green 
|
|
Operating Voltage for 100 cd/m2
|
3.1 V
|
|
Current Efficiency for 20 mA/cm2
|
4.4 cd/A
|
|
Power Efficiency for 20 mA/cm2
|
3.3 lm W−1
|
|
Device structure
|
ITO/2-TNATA (60 nm)/NPB (15 nm)/TAT* (30 nm)/ Alq3 (30 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al (200 nm) [6]
|
|
Colour
|
Deep Blue 
|
|
EQE at 10 mA/cm2
|
7.18
|
|
Current Efficiency at 10 mA/cm2
|
3.64 cd/A
|
|
Power Efficiency at 10 mA/cm2
|
1.87 lm W−1
|
|
Device structure
|
ITO/[F4-TCNQ(x nm)/m-MTDATA(y nm)]n/NPB/Alq3/Bphen/Cs2CO3/Al [7]
|
|
Colour
|
Green 
|
|
Max. Luminance
|
23,500 cd/m2
|
|
Max. Current Efficiency
|
7.0 cd/A
|
|
Max. Power Efficiency
|
4.46 lm W−1
|
|
Device structure
|
ITO/NPB (30 nm)/CBP:8 wt% (t-bt)2Ir(acac)* (15 nm)/
BPhen(35 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/CoPc:C60 (4:1) (5 nm)/
MoO3 (5 nm)/NPB(30 nm)/CBP:8 wt% (t-bt)2Ir(acac)* (15 nm)/
BPhen (35 nm)/Mg:Ag (100 nm) [8]
|
|
Colour
|
Yellow 
|
|
Max. EQE
|
16.78%
|
|
Max. Luminance
|
42,236 cd/m2
|
|
Max. Current Efficiency
|
50.2 cd/A
|
|
Max. Power Efficiency
|
12.9 lm W−1
|
|
Device structure
|
ITO/NPB (60 nm)/BNA:2 wt% perylene and 0.5 wt% DCJTB* (35 nm)/Alq3 (25 nm)/Mg:Ag (200 nm) [9]
|
|
Colour
|
White 
|
|
Max. Luminance
|
4,100 cd/m2
|
|
Max. Current Efficiency
|
1.65 cd/A
|
|
Device structure
|
ITO (100 nm)/NPB (40 nm)/ADN:C6:DCJTB (30 nm)/Alq (30 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al (100 nm)
|
|
Colour
|
Red 
|
|
Max. Luminance
|
13, 000 cd/m2 [10]
|
|
Max. Current Efficiency
|
4.9 cd/A
|
*For chemical structure information please refer to the cited references.
Characterisation
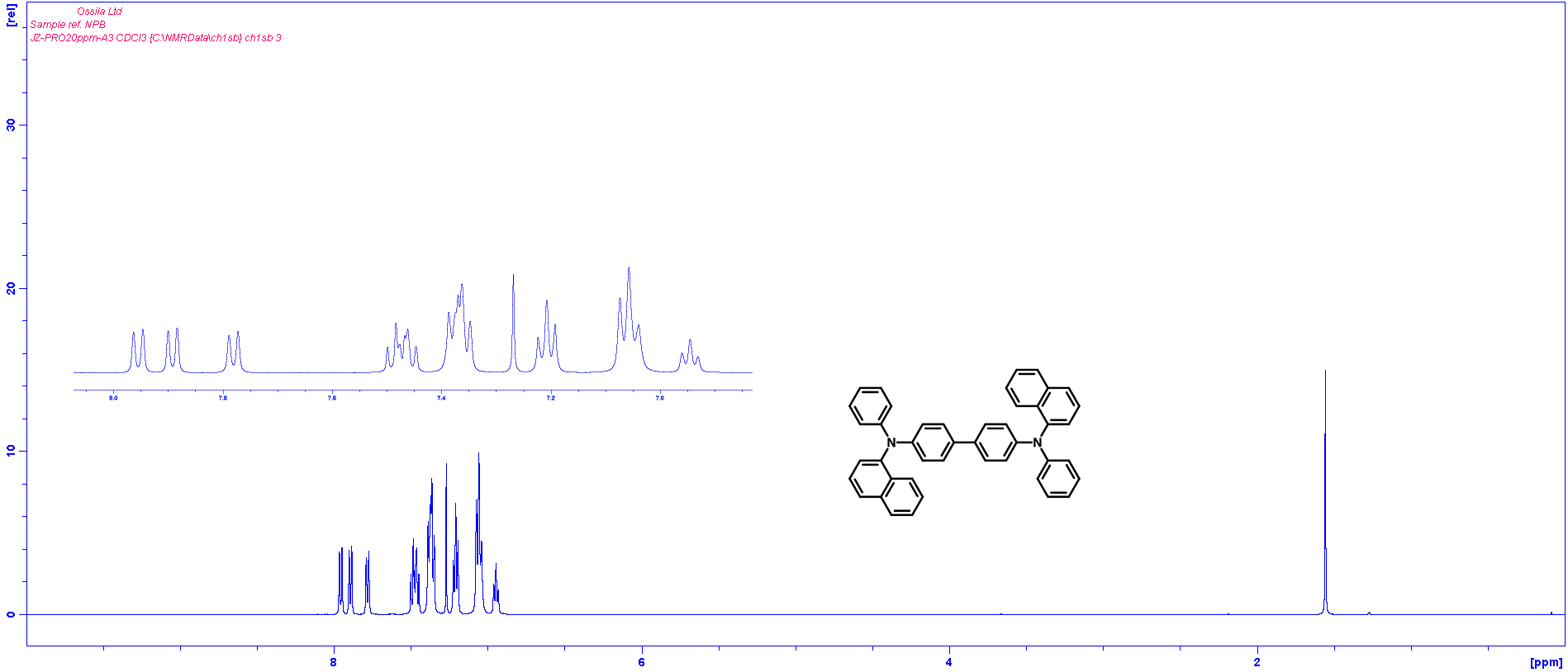 1H NMR of N,N′-Di(1-naphthyl)-N,N′-diphenyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4,4′-diamine (NPB) in CDCl3
1H NMR of N,N′-Di(1-naphthyl)-N,N′-diphenyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4,4′-diamine (NPB) in CDCl3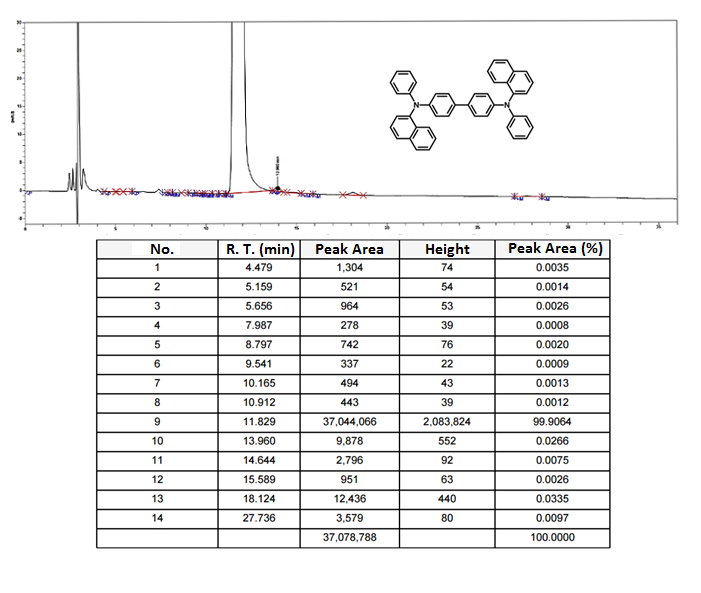 HPLC trace of N,N′-Di(1-naphthyl)-N,N′-diphenyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4,4′-diamine (NPB)
HPLC trace of N,N′-Di(1-naphthyl)-N,N′-diphenyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4,4′-diamine (NPB)


 Chemical structure of N,N′-Di(1-naphthyl)-N,N′-diphenyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4,4′-diamine (NPB)
Chemical structure of N,N′-Di(1-naphthyl)-N,N′-diphenyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4,4′-diamine (NPB)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
 1H NMR of N,N′-Di(1-naphthyl)-N,N′-diphenyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4,4′-diamine (NPB) in CDCl3
1H NMR of N,N′-Di(1-naphthyl)-N,N′-diphenyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4,4′-diamine (NPB) in CDCl3 HPLC trace of N,N′-Di(1-naphthyl)-N,N′-diphenyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4,4′-diamine (NPB)
HPLC trace of N,N′-Di(1-naphthyl)-N,N′-diphenyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4,4′-diamine (NPB)